Volume - Data Entry | Pipes (Oilfield)
The "Volume" module allows the quick computation of:
- The casing, liner, stab-In and plug cementing
- The annular volume between two strings of pipe or between a string of pipe and OH
- The capacity of a string of pipe, an open hole, or a combination of both.
- The bottom up and rat hole volume for a drilling or coiled tubing string.
- Casing and Liner Cementing Jobs
- Cement Plug Jobs
- CT Cement Plug Jobs
- Annular volume between Pipe/Hole and a CT string as well as the CT capacity taking in consideration a CT reel volume at surface.
- Pipes / Open Hole volumes
- Bottom-Up and rat hole volumes for drilling, coiled tubing or any other pipe type.
The outer sections can all be open hole, pipes or a mix of both.
The depths against each section represent the depth of the bottom of this section and NOT the length of the section.
The pipe sections can be of different type (casing, DP, Tubing or Coiled Tubing), sizes (OD and ID), wall thickness and weight.
The Pipes (Oilfield) App includes a database of all API casings, drill pipes and tubings. It also includes the most common coiled tubing and open hole sizes.
for the “”Cem. Vol”, “Annular Vol.” and “Bottom-Up” calculations, two strings need to be defined:
- The Outer String and
- The Inner String
While the inner string should only be composed of three pipe sections, the outer string can include a combination of one or more open hole and pipe section.
The toggle switch (1) is used to switch between the outer and the inner strings.
When switching strings the pipes and open holes defined in each string will be loaded in the input area (6).
The below steps shall be followed to add the desired pipe/OH to the corresponding section of the outer pipe/OH string :
- Set switch (1) to ON to allow saving pipe/OH data to outer string (The color of the buttons in the input section (6) will change to red to confirm that entry is being made to outer string)
- Press the desired pipe/OH string in the input section (6)
- Follow the “Select Section” instructions.
- Set switch (1) to OFF to allow saving pipe data to inner string (The color of the buttons in the input section (6) will change to black to confirm that entry is being made to inner string)
- Press the desired pipe/OH string in the input section (6)
- Follow the “Select Section” instructions.
Notes :
- The bottom depth of the inner string must be equal or less than the bottom depth of the outer string.
- It is optional to enter all three pipe/OH sections in the strings so, you can enter either one, two or three pipe sections.
- If you elected to enter only one or two pipe sections, you needs to input the corresponding end-of-pipe depth of these sections only.
The segment control (2) and the switches (3), (4) and (5) are then used to switch between the different calculation modes.
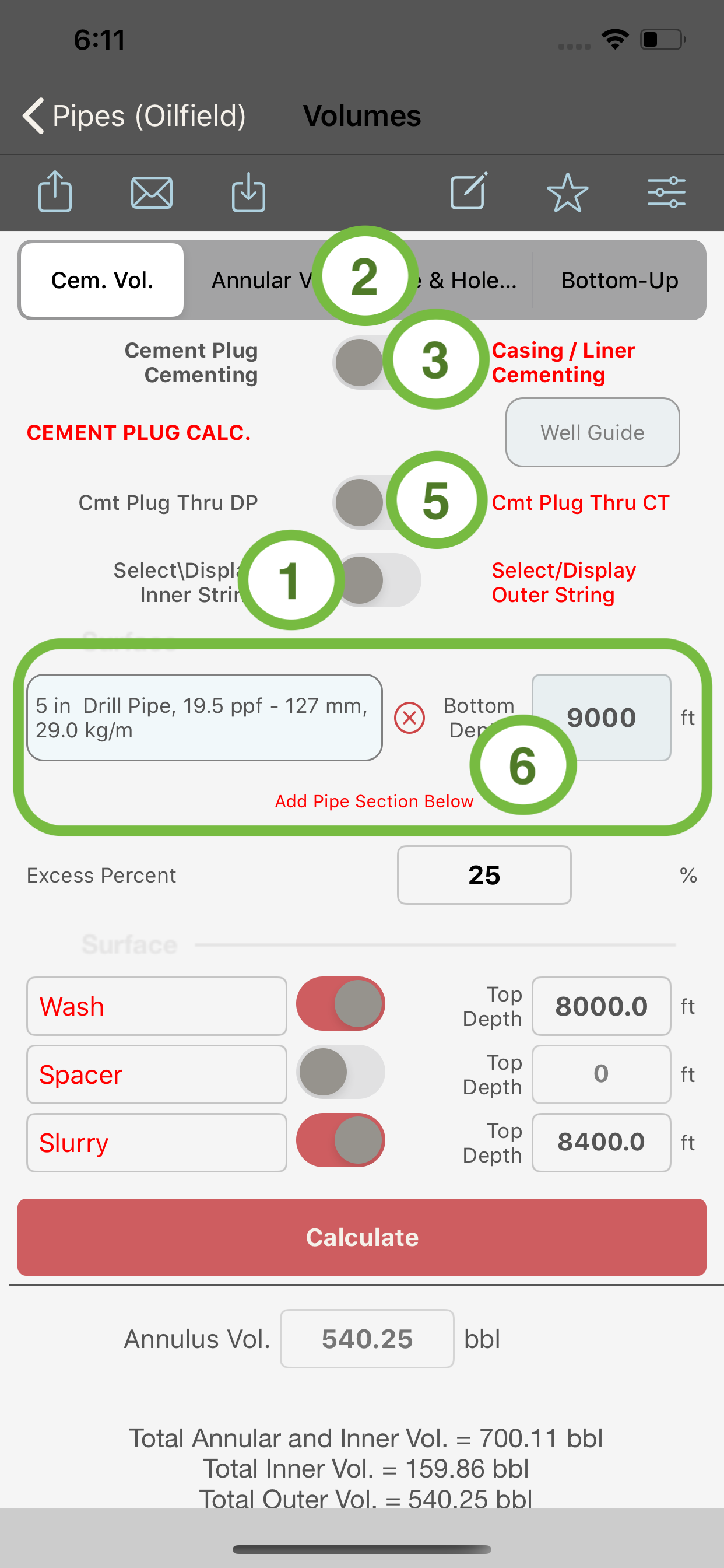
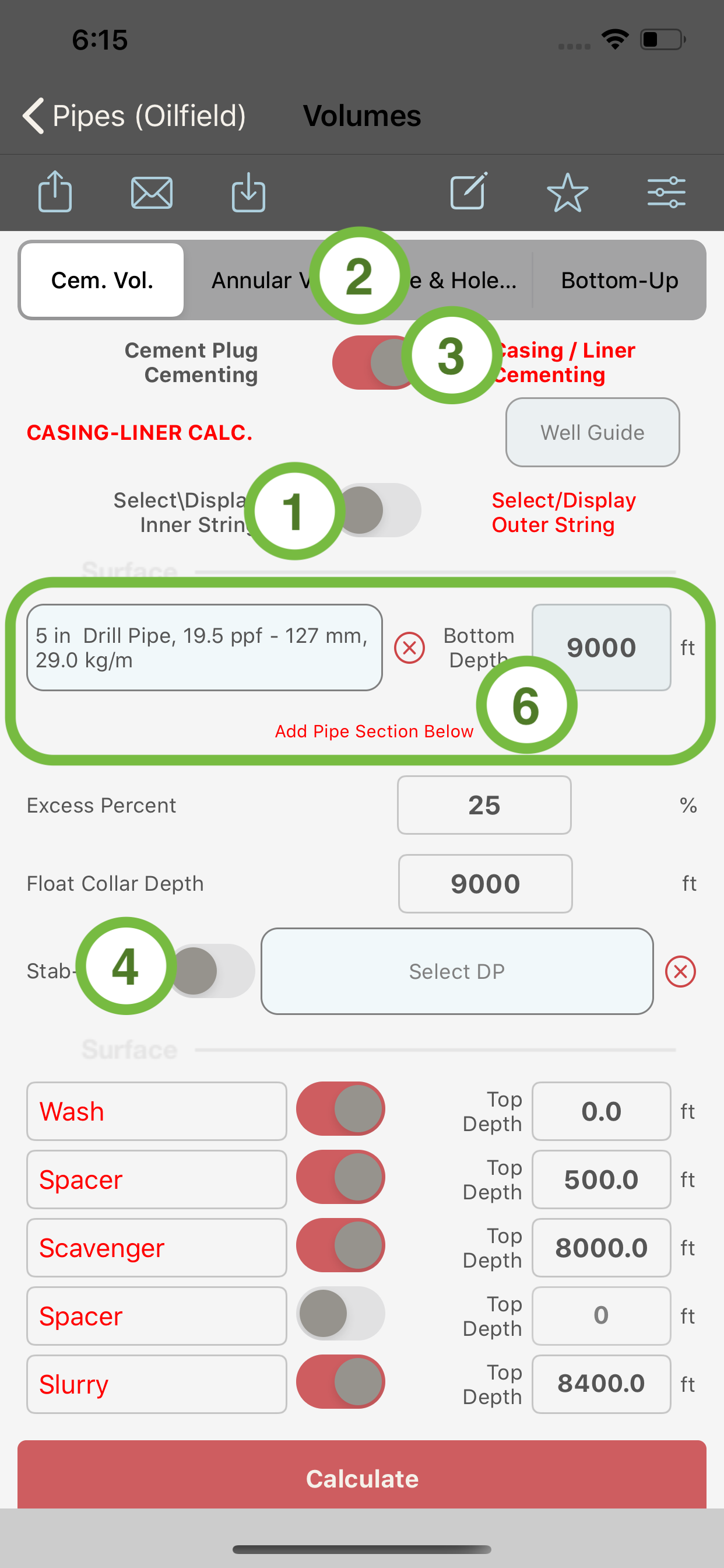
When “Cem. Vol.” is selected in the segment control (2) and :
- the switches (3) and (4) are set to ON, the module will compute the volumes for a stab-in cementing job and the stab-in string selection will be enabled. The stab-In string MUST be of a drill pipe type.
- switch (3) is ON and the stab-in switch (4) is OFF, the module will compute the volumes for a primary cementing or a liner job. In such case, the stab-in string selection will be disabled.
- switch (3) is turned OFF, the module will compute the volumes for a cement plug job. Only three fluids are available when computing cement plug volumes, these fluids are; wash, spacer and cement. Also in this case, the coiled tubing string will be available to allow the calculation of the volumes for a cement plug through coiled tubing job as follows:
- if the CT switch (5) is ON, the option to input a CT reel and the length of the reel will be accessible and a calculation of a cement plug through CT will be run. The placement of cement plug thru CT assumes that:
- the coiled tubing will be POOH once the cement exits the end of the CT
- the end of the pipe will be just below the required top of cement at the end of cement pumping.
- the top of cement provided in the data entry is considered the top of cement without pipe and so is the volume volume of cement computed.
- the displacement volume is equal to the CT reel capacity.
- if the CT switch (5) is OFF, the option to input a CT reel and the length of the reel will not be accessible and the calculation of a balanced plug through DP will be run. The placement of cement plug assumes that:
- the top of the cement provided is the required top of cement without pipe in the hole.
- the displacement volume is calculated to balance the plug while the pipe is at the plug setting depth.
An open hole excess can be used in the computation of the open hole volume (the excess can also be applied to the pipe sections if this option is selected in the settings screen) else, it will be only applied to the OH volumes. The excess percent can be then entered in the textfield in the input section (6).
When “Annular Vol.” is selected in the segment control (2), both the outer and inner strings will be available for data entry and the volumes of the annulus between both strings will be then computed.
The annular volume of up to five different fluids can be entered and computed. The name of each fluid can be edited by the user in the corresponding textfield. This new name will be used when when the output is calculated.
An open hole excess can be used in the computation of the annular volume (the excess can also be applied to the pipe sections if this option is selected in the settings screen) else it will be only applied to the OH. The excess percent is entered in the textfield in the input section (6).
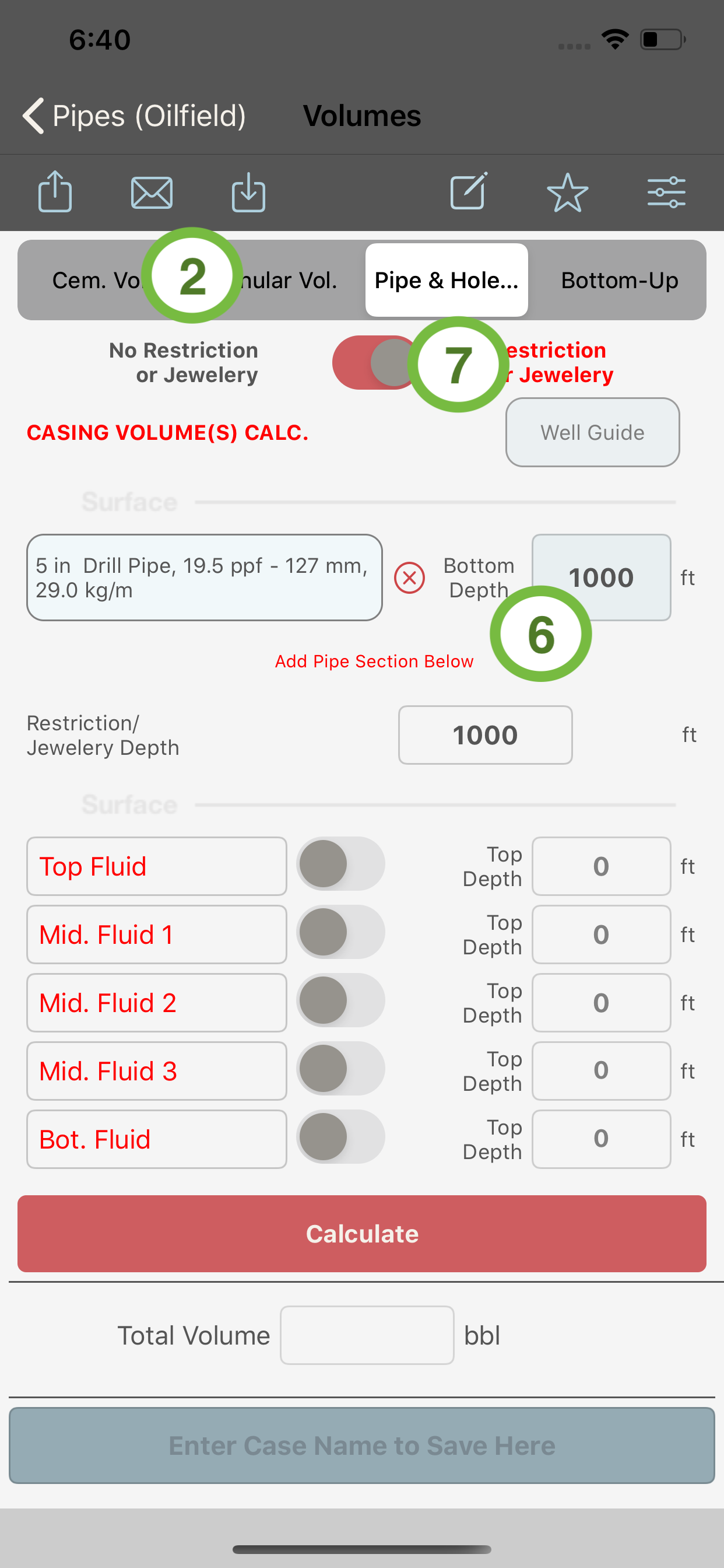
When “Pipe & Hole Vol.” is selected in the segment control (2), only one string of pipe (with a possibility to include an open hole section) will be available for data entry and the inner capacity of the string will be then computed. No excess can be applied to the inner volumes even if an open hole is entered as one of the sections.
Also, the volume of up to five fluids inside the inner pipe can be computed. The name of each fluid can be entered by the user in the corresponding textfield. This name will be used when exporting the data via email or shared.
- If switch (7) is set to ON, the module will compute the inner pipe capacity down to the defined restriction depth only. This calculation can also be useful when computing the volumes down to a specific depth or down to a restriction in the pipes. In such case the point of concern shall be entered as the collar depth.
- If switch (7) is set to OFF, the module will compute the inner pipe capacity down to the bottom of the pipe string.
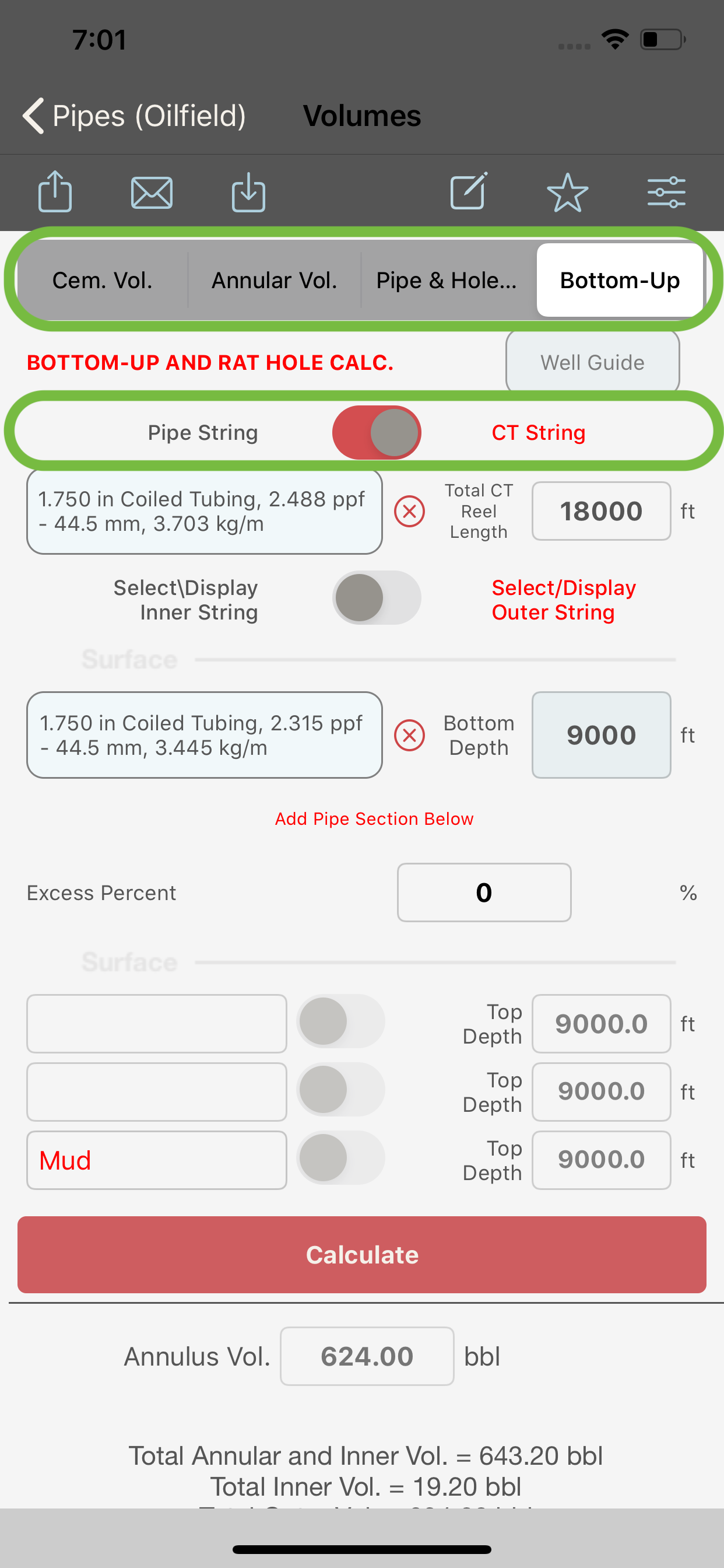
When “Bottom-Up Vol.” is selected in the segment control (2) and :
- switch (3) is turned OFF, the module will compute the Bottom-Up volume. If a Rat-Hole is present, its volume will be displayed in the output section.
- If the Coiled Tubing switch is turned ON, the module will compute the Bottom-Up volume for a coiled tubing string run in the hole and If a Rat-Hole is present, its volume will be displayed in the output section.
See below the different type of volume calculations and their segment-control and switches settings.
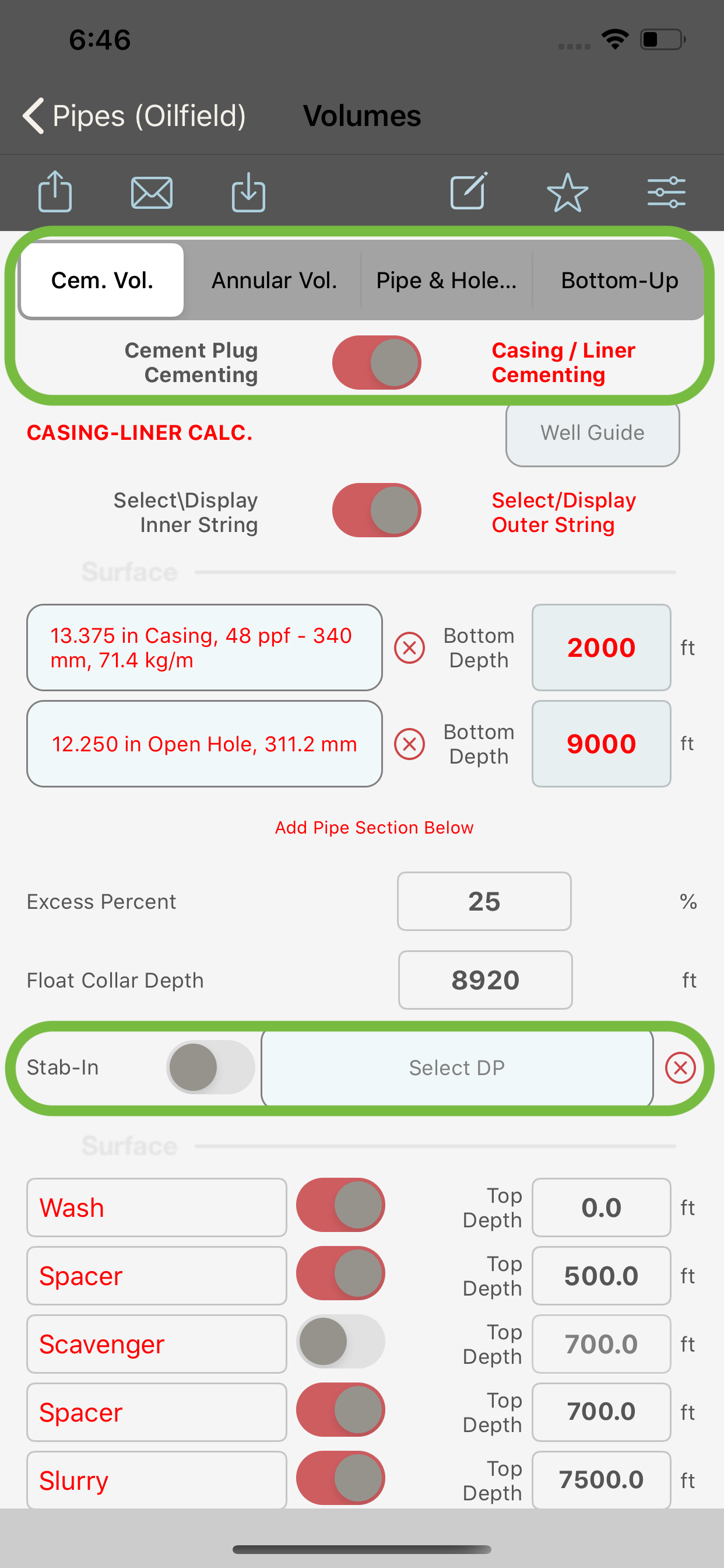
Primary Casing & Liner Cementing
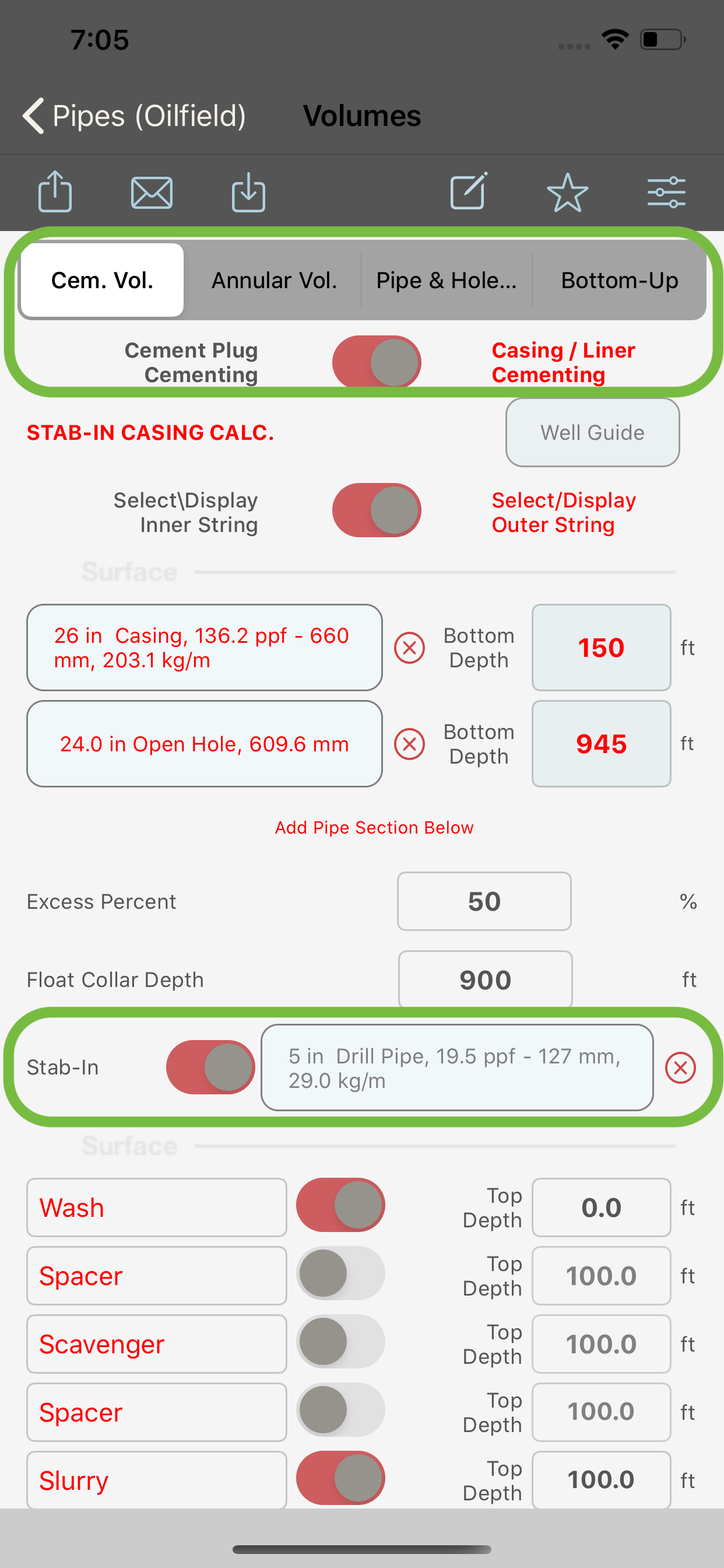
Stab In Primary Cementing
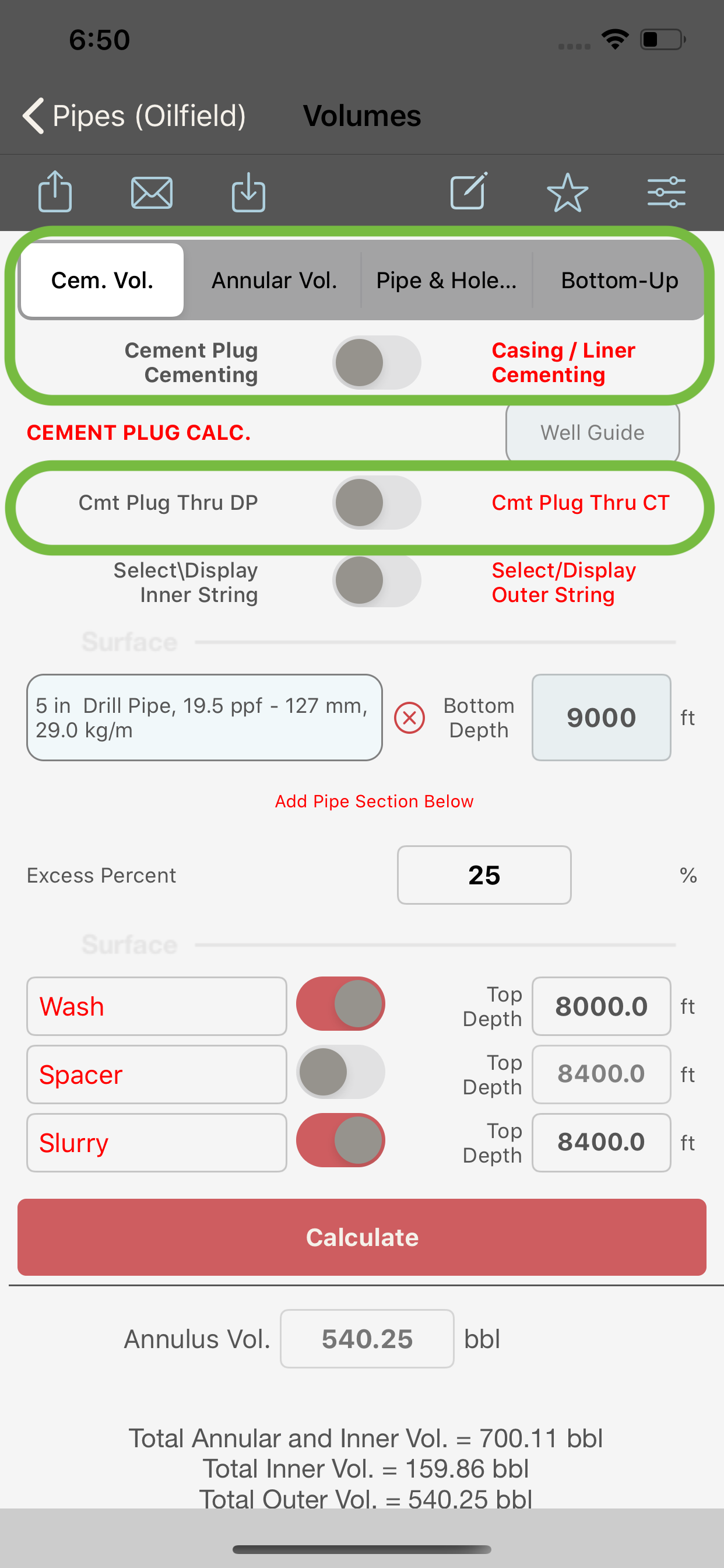
Cement Plug
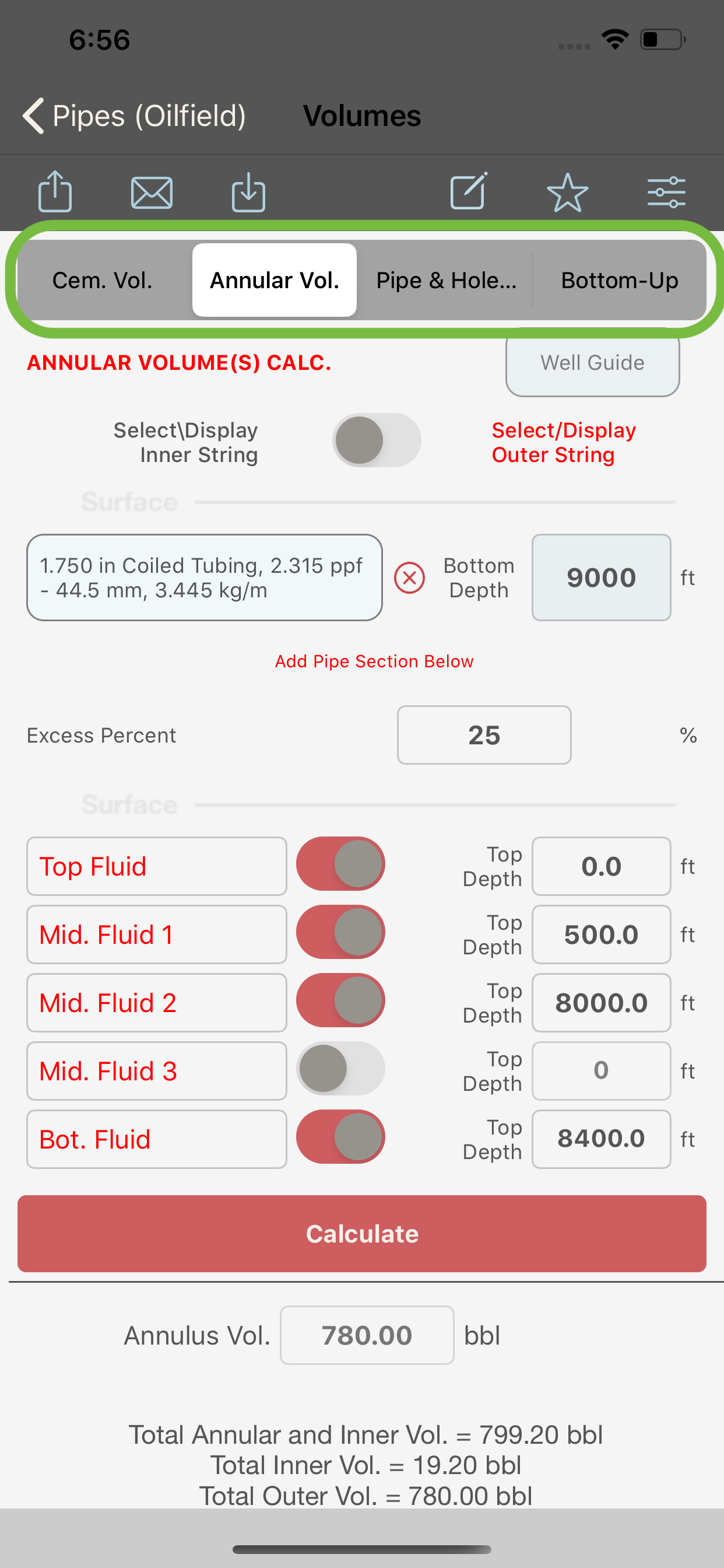
Annular Volume Calculation
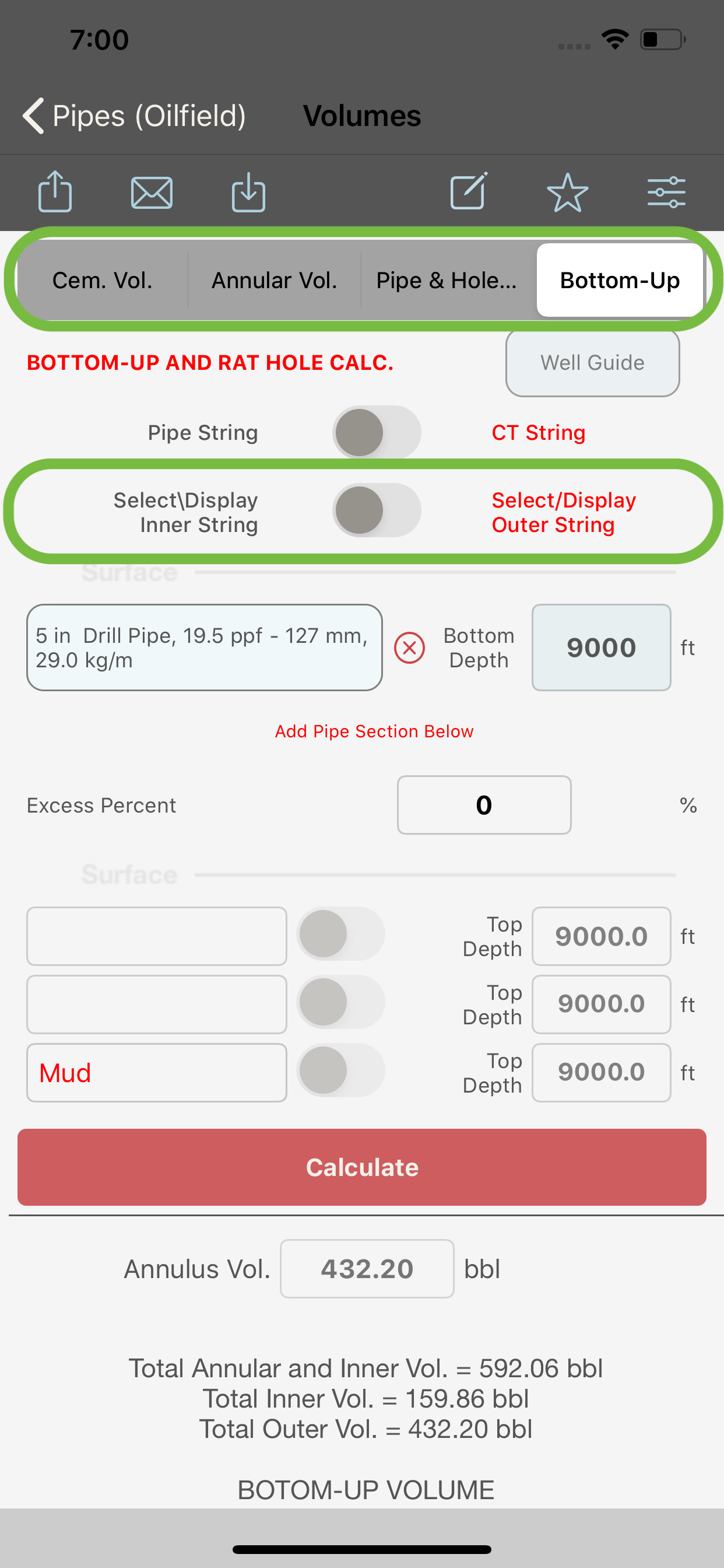
Bottom Up Calculation
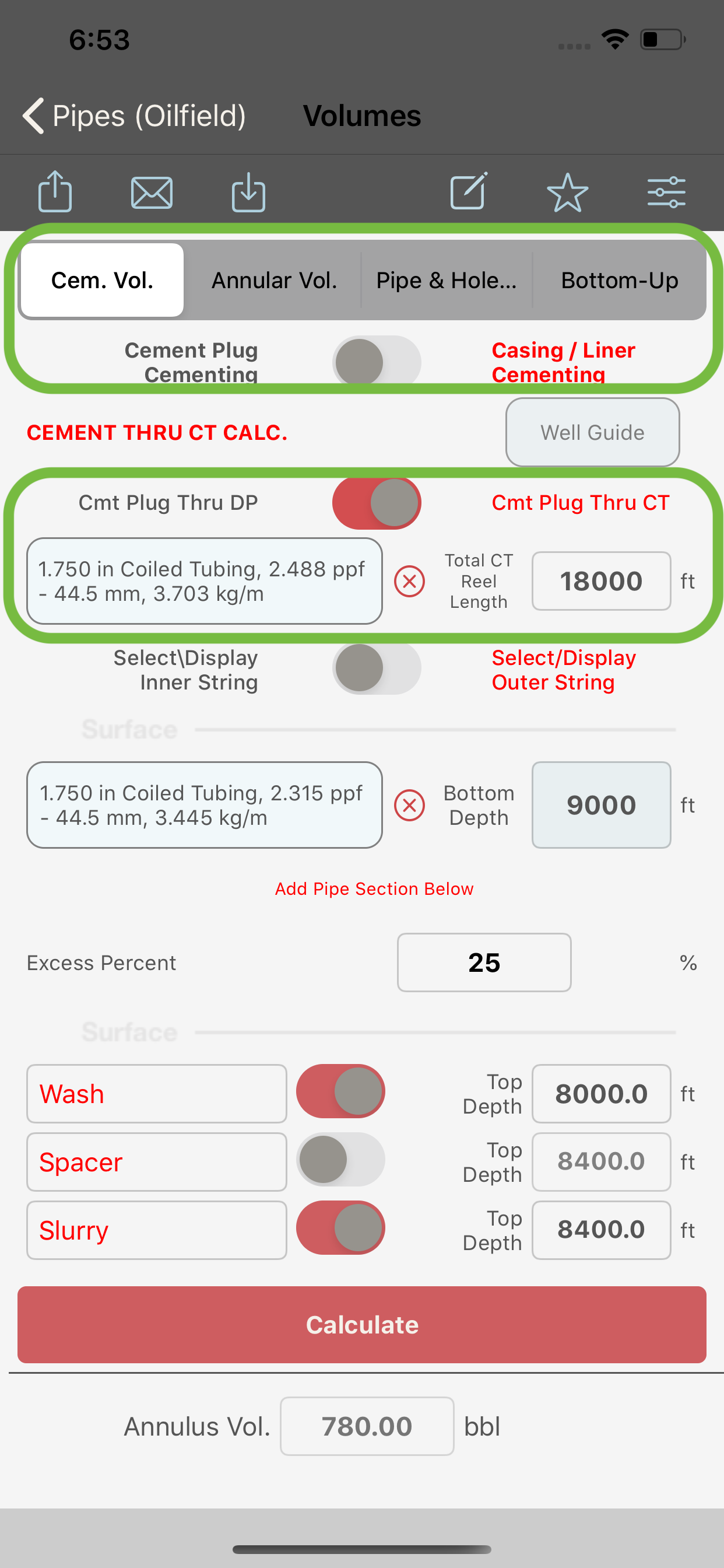
Cement Plug Thru CT
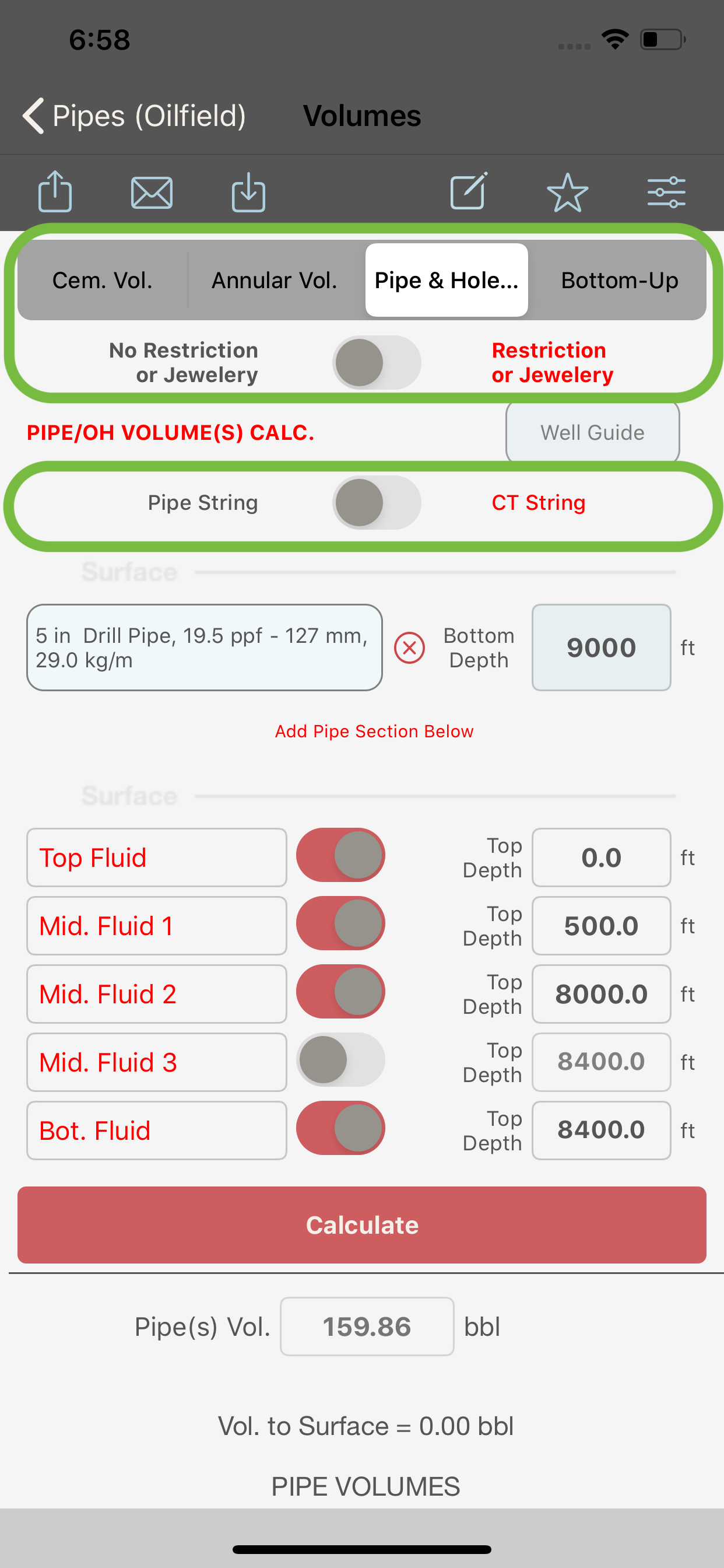
Pipe / OH Volume Calculation